Do you know there are around 3.5 million sole traders in the UK which makes 59% of the UK’s private sector business population. And with the passage of time, more people are entering into this business structure. So, if you want to set up your business as a sole trader or you’re already working as a self-employed individual, you need to know how sole trader tax works.
Before jumping into the details, you first need to know that all self-employed individuals (including the partners in partnership business) are levied taxes based on the system of self-assessment on an annual basis. With self-assessment, Income Tax and National Insurance Contributions are charged based on your earnings after deducting the expenses. Let’s start with the basics!
Accounting firms is the UK’s only instant Accountancy & Taxation Fee Comparison Website. Register Today!
Register as a Sole Trader
The first step is to register as a self-employed or sole trader with HMRC in the UK. You can use these three ways to register:
- Fill in our online registration form
- Print the registration form and post it to HMRC
- Contact HMRC on its helpline number 0300 200 3310
Self Assessment
Once you’re registered, you will be sent a self-assessment notice after the end of the tax year. Note that a tax year starts from 6th April to 5th April in the UK. A paper tax return can be submitted on 31st October after the year-end when you received the self-assessment notice.
For filing the return online, you get an extra 3 months. The last date for submitting an online return is the 31st of January, after the end of the tax year. For instance, for the tax year starting from 6th April 2020 to 5th April 2021, you need to submit a paper tax return to HMRC by 31st October 2021. If you want to submit it online, you can submit it by 31st January 2022.
The tax that you need to pay for the current tax year needs to be fully paid on or before the 31st January deadline.
Payment on Account
When you start paying taxes via self-assessment, you also need to make payments on account. These are the advanced payments that are spread into two instalments during the year and are calculated based on the previous year’s tax bill.
The first payment is made on 31st January and the second on 31st July.
Need the help of an accountant to do everything on your behalf? We’d love to help out. Get in touch with us now!
Sole Trader Taxes
After registration, you need to pay different types of taxes as a sole trader. These include:
Income Tax
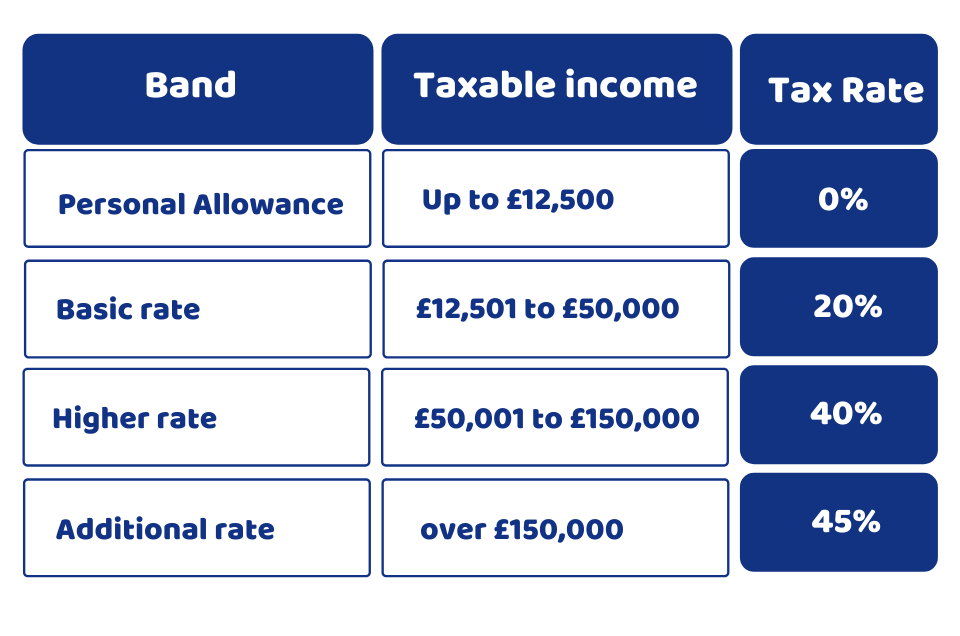
Let’s talk about the income tax first. Income tax is the tax that you need to pay as a sole trader. The government provides a personal allowance of £12,570 for you. This is the threshold on which you don’t have to pay any income tax. When your earnings exceed this amount, you need to pay the taxes are per the following:
National Insurance Contribution (NICs)
Along with income tax, you need to pay a National Insurance Contribution (NICs). The amount you pay as NIC depends upon how much you earn in a tax year. A sole trader usually pays 2 types of National Insurance: Class 2 and Class 4.
- If your profits are £6,515 or more a year (2021/22), you pay Class 2 NI £3.05 a week
- If your profits are from £9,569 to £50,270 a year, you pay Class 4 NI at the rate of 9%, and 2% on any profits above £50,270.
You can calculate the profit by deducting expenses from the income as a self-employed.
VAT
If, as a self-employed, your earnings are above £85,000 in a year, you are legally required to register your business for Value Added Tax (VAT). After registering for VAT, you will need to include VAT in all your bills. VAT that you have paid on business costs can also be reclaimed. Sometimes if you’re below the VAT threshold, it may be beneficial to register your business for VAT. It might be needed when most of your clients are business customers who want to claim back the VAT you charge them.
Quick Sum Up
We do hope that after giving this blog a read, you have understood what is sole trader tax, how you can register, how Income Tax and NICs are charged and when you need to pay them. You should also note that there are various types of allowances available to bring down the tax amount you have to pay on your business profits. In addition, you can get help from an accountant to save you from the extra tax burden.
Get help from our Qualified Accountants, Bookkeepers, Tax Experts to fulfil your legal obligations as a sole trader. Compare their Services & Fee, and Signup now in 3 minutes at Accounting Firms!
Disclaimer: This blog is written for general information on Sole Trader Taxes.